
This blue planet that we reside on is often regarded as ‘Mother Earth’ but if you look at it from a transparent perspective then we haven’t been kind to our mother. Sounds depressive but is unfortunately true. I am not denying the fact that technology has undoubtedly brought about incredible advancements and revolutionized the way we live, work, and communicate. However, the downside to this technological revolution is that it has also caused significant harm to the environment. The increasing demand for new and advanced technology, combined with humanity’s insatiable wants, has resulted in the destruction of natural habitats, increased pollution, and a significant impact on the planet’s ecosystems.
The rate at which technology is advancing and the growing demand for it has caused the widespread destruction of natural habitats, leading to the extinction of many species. Forests, wetlands, and other natural ecosystems are being destroyed to make way for technology infrastructure, such as data centers, mines, and manufacturing plants. The expansion of cities and urban areas has also led to the destruction of natural habitats, which is a significant contributor to the loss of biodiversity.
While working on Exhibit’s sustainability edition, it was impossible for me and my team to simply ignore the fact that technological developments and harm to the environment go hand in hand. Thus, making our readers aware of the environmental impact of the technological revolution became a moral duty. Here are some ways technology harms the environment followed by what we can do to curb the damage –
E-Waste
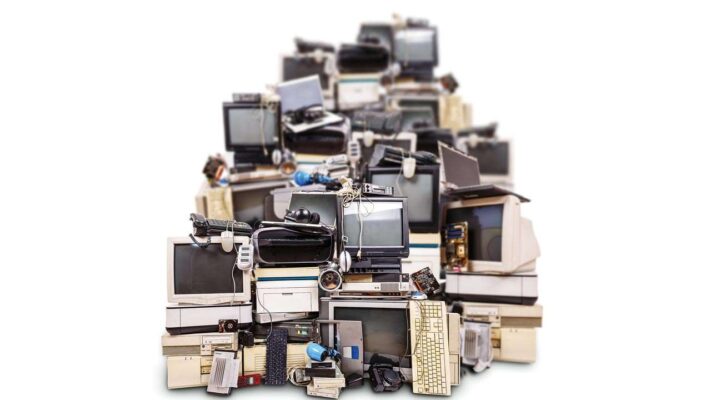

E-waste refers to electronic products that are discarded by consumers when they are no longer needed. This includes items such as computers, televisions, smartphones, and other electronic devices. According to the United Nations, approximately 50 million metric tons of e-waste is generated each year, and this number is expected to increase.
E-waste is a growing concern for several reasons. Firstly, electronic devices contain hazardous materials such as lead, mercury, and cadmium that can leach into soil and groundwater when discarded improperly. These toxins can have severe health implications for humans and animals, leading to respiratory issues, neurological damage, and cancer. Secondly, the production and disposal of electronic devices require a vast amount of energy, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and exacerbating climate change. Whereas, the production of electronic devices requires the extraction of precious metals and minerals, leading to environmental degradation and pollution.
The amount of e-waste generated worldwide is staggering. According to the Global E-waste Monitor, the world generated 53.6 million metric tons of e-waste in 2022, with Asia producing the highest amount. Unfortunately, only 17.4% of e-waste was recycled, while the rest was either disposed of in landfills or incinerated. The improper disposal of e-waste poses a significant risk to the environment and human health, making it essential to adopt proper disposal methods.
One solution to the e-waste problem is to adopt sustainable practices in the manufacturing of electronic devices. Many companies are now using recycled materials in the production of electronic devices, reducing the need for the extraction of new materials. Additionally, companies can design devices to be easily repairable and upgradable, reducing the need to discard the entire device.
Another solution is to promote the responsible disposal of e-waste. Governments can implement policies and regulations to ensure that e-waste is disposed of responsibly, such as requiring manufacturers to take back and recycle old devices. Consumers can also do their part by recycling old devices properly or donating them to charities or refurbishers.
We can also reduce e-waste by changing our consumption habits. We can opt for longer-lasting and repairable devices instead of constantly upgrading to the latest model. We can also practice responsible disposal of devices, such as donating or selling them when they are still useful.
Energy Consumption
Increased energy consumption is one of the most significant ways in which human activities are harming the environment. The use of fossil fuels to power homes, transportation, and industries has resulted in a significant increase in greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change. Energy consumption has also led to the depletion of non-renewable resources such as coal, oil, and natural gas, further exacerbating the impact on the environment.
The industrial sector is one of the largest contributors to energy consumption, with the demand for energy-intensive products and services on the rise. Many industrial processes, such as cement and steel production, require vast amounts of energy and are responsible for a significant portion of global greenhouse gas emissions. The increasing demand for consumer goods has also led to increased energy consumption, as the production and transportation of goods require energy.
The transportation sector is another significant contributor to energy consumption and environmental harm. The use of fossil fuels to power cars, trucks, and airplanes has led to a significant increase in greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change. Additionally, the construction and maintenance of transportation infrastructure, such as roads and highways, also require vast amounts of energy.
Energy consumption in households has also contributed to environmental harm. The use of electricity for heating and cooling, as well as the use of electronic devices, contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and the depletion of non-renewable resources. The increasing demand for energy-intensive appliances, such as air conditioners and refrigerators, also contributes to increased energy consumption and environmental harm.
Climate Change

The use of fossil fuels to power technology has contributed significantly to climate change. Fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, which trap heat and contribute to global warming. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, the earth’s temperature has already increased by 1 degree Celsius above pre-industrial levels, and it is projected to continue to rise.
Furthermore, the production and transportation of electronic devices also contribute to carbon emissions. According to a report by the Carbon Trust, the carbon footprint of a smartphone is around 55 kilograms of CO2 equivalent, which is equivalent to driving a car for 125 miles.
Resource Depletion

The manufacturing of electronic devices requires the use of rare metals such as cobalt, lithium, and nickel. These metals are typically mined from the earth, and the process of mining can cause significant environmental damage. For example, mining can lead to soil erosion, deforestation, and water pollution. Mining is perhaps one of the biggest contributors to environmental depletion around the world!
Furthermore, the increasing demand for high-speed internet and digital services has led to the construction of large data centers that require a vast amount of energy for cooling and power supply. Data centers have become one of the largest energy consumers worldwide, with their energy usage expected to double by 2030. This energy consumption contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and exacerbates climate change.
The good news is that there are several ways in which we can mitigate the negative impacts of technology on the environment. Here are some examples:
- Choose energy-efficient devices: Look for devices with an Energy Star certification, which indicates that they use less energy and emit fewer greenhouse gases.
- Recycle electronic devices: Many retailers and manufacturers offer recycling programs for electronic devices. When disposing of an electronic device, make sure to do so properly to avoid environmental harm.
- Use renewable energy: Consider switching to renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, to power electronic devices and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Reduce energy consumption: Unplug electronic devices when not in use, use energy-efficient settings, and turn off lights and other appliances when leaving a room.
- Encourage manufacturers to produce sustainable products: Support companies that prioritize sustainability in their manufacturing processes and use environmentally-friendly materials.
In conclusion, while technology has provided many benefits, it has also had significant negative impacts on the environment. We must take steps to mitigate these impacts, including choosing energy-efficient devices, properly recycling electronic devices, using renewable energy, reducing energy consumption, and encouraging manufacturers to produce sustainable products. By doing so, we can help protect the environment for future generations.


Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?