The two-stroke and the four-stroke engine
Massive transformations have taken place in automotive engines in the past few decades, but the two main internal combustion engine designs remain the 2-stroke and the 4-stroke. While we reckon that you’ve at least heard these terms before, do you really know the difference between them? How do they work, and which is better? Read on to know more!
How Does a Combustion Engine Work, and What Is a “Stroke” Anyways?
In order to understand how different these two engines are, you need to first understand the basics of how an engine works. Combustion, also known as the process of burning fuel, is the underlying chemical process involving releasing energy from the mixture of air & fuel. In an internal combustion engine (ICE), the ignition and combustion of the fuel occur within the engine itself. The engine then partially converts this energy from the combustion to work up. The engine consists of a fixed cylinder and a moving piston. The expanding combustion gases push the piston, which in turn rotates the crankshaft. Ultimately, through a system of gears in the powertrain, this motion drives the vehicle’s wheels. A stroke is when the piston moves up & down to complete a revolution. This revolution or the combustion cycle is the complete process in which fuel & air is mixed and sucked in the piston chamber, ignited and expelling exhaust gases. This process takes place in four different steps mainly-
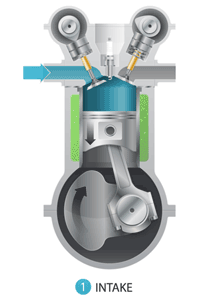
Intake
: When the piston moves down the cylinder, it allows a mixture of fuel and air into the combustion chamber.
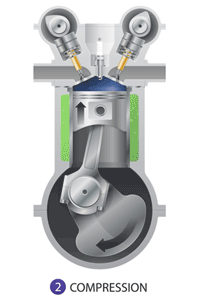
Compression
: When the piston moves back up the cylinder, the intake valve is closed to compress the gasses within.
Combustion
: A spark from the spark plug ignites this mixture.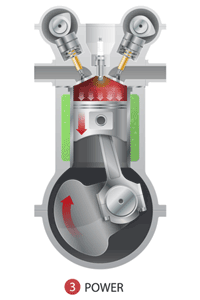
Exhaust
: When the piston goes back up the cylinder and the exhaust valve is opened, the combusted gases are released via the exhaust.

Two-stroke vs four-stroke
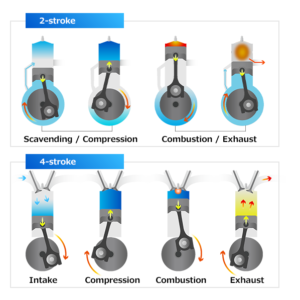
The Difference between a 2-stroke and a 4-stroke engine is how quickly this combustion cycle process takes place, based on the number of times the piston moves up and down during each cycle.
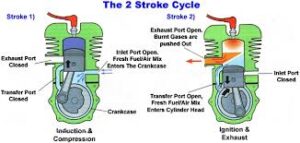
In a 2-stroke engine, the entire combustion cycle is completed within a single piston stroke: a compression stroke followed by the combustion of the compressed fuel. During the return stroke, the exhaust is let out, and a fresh fuel mixture enters the cylinder. The spark plugs fire once every single revolution, and power is produced once every 2-strokes of the piston. It has one revolution of the crankshaft during one power stroke, and due to the larger power-to-weight ratio, it generates higher torque as compared to four-stroke engines. It uses ports for fuel’s outlet and inlet, and is usually less efficient and produces more smoke. Two-stroke engines also require more lubricating oil to be pre-mixed in with the fuel, as it burns with it.

In a 4-stroke engine, the piston completes 2-strokes during each revolution: one compression stroke and one exhaust stroke, each being followed by a return stroke which means it has two revolutions of the crankshaft during each power stroke. The spark plugs fire only once every other revolution, and power is produced every 4-strokes of the piston. Compared to the ports used in two-stroke engines, the four-stroke engine uses valves for the inlet and outlet of fuel, resulting in higher thermal efficiency while generating less torque. It is more efficient in burning the fuel, it emits less smoke and has comparatively less wear & tear of the parts. These engines also do not require pre-mixing of fuel and oil, as they have a separate compartment for the oil.
So, which is ‘better and which one to choose?
Here are a few of the pros and cons of both engine designs:
- As far as efficiency goes, the 4-stroke certainly ranks up the chart due to the fact that fuel is consumed once every four strokes.
- Four-stroke engines are heavier due to more components & can weigh up to 50% more than a comparable 2stroke engine, adding a lot of difference to the overall riding dynamics of the vehicle.
- Typically, a 2-stroke engine creates more torque at a higher RPM, while a 4-stroke engine creates a higher torque at a lower RPM.
- BRRRAAAAPPPPP!!! The 4-stroke engine is also much quieter; a 2-stroke engine is significantly louder and has a distinctive, high-pitched “buzzing” sound.
- Because 2-stroke engines are designed to run at a higher RPM, they also tend to wear out faster; a 4-stroke engine is generally more durable in comparison. That being said, 2-stroke engines are more powerful as the initial torque can blow the mind away!
- Two-stroke engines are of much simpler design as compared to the complexity of four-stroke engines, making them easier to fix. They do not have valves but rather ports. Four-stroke engines have more parts; therefore, they are more expensive, and the maintenance costs more.
- Two-stroke engines require pre-mixing of oil and fuel, while the 4-strokes do not.
- Four-strokes are more environmentally friendly; in a 2-stroke engine, burnt oil is also released into the air with the exhaust.
 So which is better and which one to prefer completely depends on the application and preference of usage. Two-stroke engines are typically found in smaller applications such as remote-controlled cars, lawnmowers & tools like chainsaws, boat motors and dirt bikes. Four-stroke engines are found in anything from go-karts, sportbikes right up to the typical internal combustion engine in your cars. It’s up to you to decide which engine you prefer and for what purpose.
So which is better and which one to prefer completely depends on the application and preference of usage. Two-stroke engines are typically found in smaller applications such as remote-controlled cars, lawnmowers & tools like chainsaws, boat motors and dirt bikes. Four-stroke engines are found in anything from go-karts, sportbikes right up to the typical internal combustion engine in your cars. It’s up to you to decide which engine you prefer and for what purpose.


When I initially commented I clicked the “Notify me when new comments are added” checkbox and now
each time a comment is added I get several emails with the
same comment. Is there any way you can remove people from that service?
Many thanks!